ALUMINUM BATTERY Aluminum's emergence in battery technology: A lithium alternative?
Related Vendors
Aluminum (Z = 13) is a popular conductor, applicable in various electronics and electrical applications. The use of aluminum in EV batteries is hard to imagine. In reality, such aluminum-based batteries are available in the market. The article explains aluminum-based batteries and their potential to stand out in the lithium-ion-dominated EV industry.

Why Aluminum rather than Lithium?
Aluminum (Z = 13) is a metal exhibiting an electrical conductivity of 3.8 x 107 S/m. After silver, copper, and gold, aluminum is the fourth most conductive element in the periodic table.
The excellent electrical conductivity, light-weightedness, transformable shape, mechanical properties, and affordable price make Al an excellent choice for commercial use. Applications of aluminum include conductive materials, bus bars, overhead transmission lines, underground wiring, and appliance connections.
Aluminum in battery technology
Lithium-ion batteries rule the EV industry. Lithium is a rare and expensive material. Aluminum is among the most abundant materials on earth. Using aluminum-based batteries would drastically reduce costs. Aluminum-based batteries are a subject of research — not yet commercially introduced in the market.
Certain combinations of aluminum with other metals make up different battery types. Some aluminum battery technologies are: aluminum-ion battery, aluminum-air battery, aluminum-chlorine, aluminum-sulfur, aluminum-iron-oxide, aluminum-copper-oxide, aluminum-iron-hydroxide, and aluminum-manganese dioxide. The most popular ones, on the verge of widespread commercial use, are aluminum-ion batteries.
Aluminum-ion batteries: Rechargeable batteries
Aluminum-ion batteries are commonly known as AIB batteries or simply AIBs. Aluminum-ion batteries are rechargeable, using aluminum ions to store charge.
Aluminum-ion battery chemistry
Chemically, both Lithium (Z = 3) and Aluminum (Z = 13) are electropositive metals. Lithium quickly lets off its one electron to become a Li+ cation or simply a positively charged ion. Similarly, Al donates three electrons to become an Al3+ cation. Lithium has a valency of 1 and aluminum has a valency of 3. The atomic radii of both elements are also similar. However, aluminum is slightly bigger than lithium.
Aluminum-ion battery structure
In aluminum-ion batteries, pure aluminum metal or aluminum alloys function as the anode. Graphite is a commonly used cathode. Some other cathode materials include titanium nitride, vanadium dioxide, and sulfur-based materials.
The aluminum-ion battery structure consists of two electrodes separated in an electrolytic solution. Conventional designs use liquid electrolytic solutions made from acidic room temperature non-aqueous ionic liquids. Some newer battery designs use solid-state electrolytes (in salt forms).
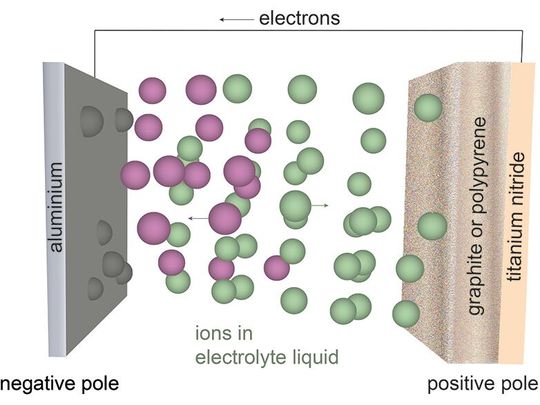
The anode remains the source of aluminum-ion generation. The insertion of one Al3+ ion is equivalent to three Li+ ions. As a result, AIB batteries exhibit a higher volumetric capacity compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Benefits of Aluminum-ion batteries
Transferring three units of charge through one ion increases the energy storage capacity of aluminum-ion batteries. Theoretically, the energy density becomes 50x more than Lithium. It means that AIB batteries can charge faster and last longer than lithium-ion batteries.
Limitations of Aluminum-ion batteries
Redox reactions, anode corrosion, dendrite formation, and passivation can damage the battery over time. The cathode tends to showcase insufficient capacity and poor cycling stability. The practical volumetric capacity reduces more than lithium-ion batteries. Aluminum-ion batteries have a low energy density and short shelf-life for EV and grid use.
:quality(80):fill(efefef,0)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/62/0c/620cfcbf6f486/titelbild-webkon-pb-2022-03-15.jpeg)
WEB CONFERENCE: ENERGY STORAGE
Keys to the design and operation of battery storage systems
Properties of aluminum-ion batteries
As mentioned above, aluminum is an abundant material. Aluminum-based batteries would cost 25 % less than rarely available lithium. Practically, aluminum-ion batteries exhibit the following properties.
- Rechargeability: A large number of charging-discharging cycles.
- Small size.
- Low cost.
- Recyclability.
- Better high-temperature performance.
- High safety due to low flammability.
- Limited battery life.
- Lower voltage output.
- Decreased efficiency and output.
- Less effective in EVs and grids.
Developments in Aluminum-ion batteries
As of 2025, aluminum-ion batteries have not been commercialized yet. The technology is in the development stages. The section lists recent breakthroughs in developing efficient AIB batteries.
MIT effort
In 2022, engineers at MIT developed a battery using Aluminum anode and sulfur cathode in molten chloro-aluminate salt electrolyte. The resulting battery was found to withstand hundreds of charging cycles and offer fast charging at a temperature of 200 degrees Celsius.
The battery would work better at higher temperatures. The low melting point of salt electrolyte prevents dendrite formation — a common problem in Li-ion batteries. The engineers believe that these aluminum-ion batteries can empower homes and EV charging stations. However, the technology awaits commercialization.
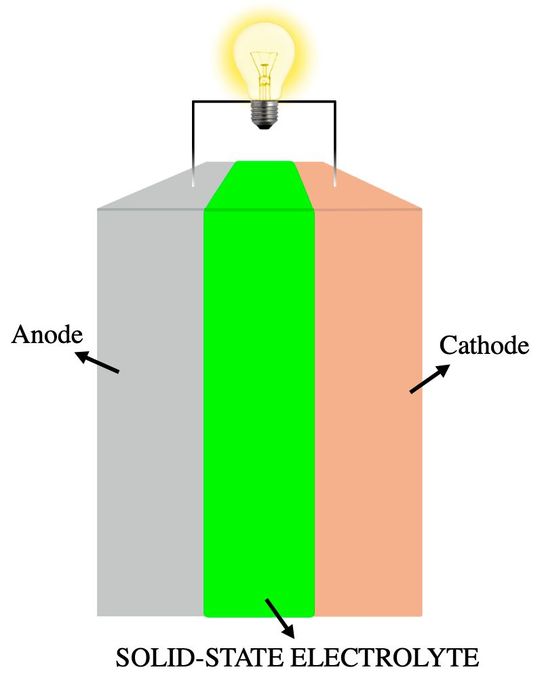
Solid-state Electrolyte Attempt
In 2025, Researchers from Beijing used a solid-state electrolyte in aluminum-ion batteries. Instead of ionic liquid and polymer electrolytes, they used a solid-state electrolyte made from porous aluminum fluoride salt. Fluoroethylene carbonate additive functioned like a protective coating to enhance the stability and longevity of the battery.
As a result, the electrolyte improved overall battery conductivity and performance. The aluminum-ion battery showed 99 % capacity after 10,000 cycles. Li-ion batteries typically show 80 % capacity after 300-500 cycles. The battery was recyclable, reducing environmental impact and cutting costs of the renewable energy system.
SEI Study
Researchers at the University of Queensland, Australia have improved performance and stability in aluminum-ion batteries. The researchers investigated the performance of solid-electrolyte interphase “SEI”. They planned to use different aluminum-alloy chemistries to optimize SEI stability. Using pre-cycling to improve SEI eliminated dendrite formation, paving the way for AIB battery commercialization.
Aluminum-air batteries: Non-rechargeable batteries
Aluminum-air batteries are another aluminum-based battery technology. Unlike aluminum-ion batteries, aluminum-air batteries and their hybrids are commercially available in some parts of the world. Aluminum-air batteries use air as a medium to produce electricity. In battery technology, aluminum functions as the negative electrode, and oxygen in the air behaves like the positive electrode. The reaction between oxygen and aluminum produces electricity.
In some aluminum-air battery technologies, water takes part in the reaction to enhance recyclability and reusability. Aluminum-air batteries are non-rechargeable, they do not store charge. These batteries exhibit a very high energy density of about 1300 W.h/kg, much higher than Lithium-ion and other commercially used battery technologies. Limitations include high anode costs and excessive amount of byproduct generation.
References
(ID:50333128)



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/71/fd/71fdcc22d9a9bd2f42985f692c4aefa2/0128924236v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/94/54/94548eaecd020681e558d563bc48ba1d/0128926221v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/29/99/2999bb9af245dd31f4c837c1d9359046/0128923137v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/10/78/107856328ef320cc081bf88e0baf95e8/0128685487v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/67/62/676279913d77e1db48eb5cbe9be4c767/0128937895v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/0f/a2/0fa2b5bdc21e408fd73e637d226d5210/0128681532v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4f/6f/4f6faf0ca6f748a2967d6b5bba7c88e1/0128682406v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ad/52/ad52f7b5542eff15ba54ec354d31b50d/0128681536v4.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1e/9c/1e9c45d6fcf2fb48dc47756e4cb20174/0128931043v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/8b/42/8b4271e1bedea432ab03c83959e30431/0128818204v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/87/5a/875a8fa395c1eec9677e075fae7f5e8e/0128793884v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/2f/93/2f9364112e8c6ff38c26f9ba34d0f692/0128791306v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3c/d1/3cd1cacbceb792ba63727199c61ca434/0127801860v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/5a/a0/5aa0436498af618297961fd54ab36cdf/0126290792v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/cb/30/cb30ebdca7fcaea281749cb396654eb3/0124716339v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/0b/b4/0bb4cdfa862043eac04c6a195e59b3e0/0124131782v2.jpeg)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/5f/71/5f71d5f92a5f6/2000px-rogers-corporation-logo-svg.png)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/62/95/6295c25c8dc1a/schunk-sonosystems-300dpi.png)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/66/8b/668becd1c07eb/dowa-logo-word--1-.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/82/14/82142acb974664ccbf755d77be6fe881/0126347614v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/7c/58/7c58cec56e63a63af024e58dd8930e23/0126563932v2.jpeg)