POWER TRANSISTORS GaN HEMT Vs SiC MOSFET: Brief Comparison
Related Vendors
GaN HEMT and SiC MOSFETs have attracted worldwide attention due to their efficiency and high-power performance. The article compares GaN HEMTs and SiC MOSFETs based on operation, properties, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.

GaN HEMT: Emerging semiconducting technology
HEMT
In order to understand GaN HEMT, let us first look at what HEMTs are. HEMT or High Electron Mobility Transistor is a type of FET (Field Effect Transistor) consisting of a heterojunction. The junction is made between two materials with different band gaps. A combination of GaAs and AlGaAs, two semiconducting materials, of varying band gaps is widely used in the industry.
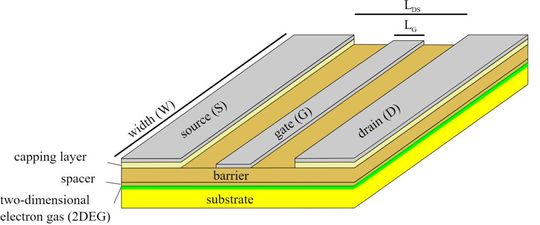
One of the biggest advantages of HEMTs is that they are capable of operating at high frequencies. The manufacturing process forms a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) layer at the heterojunction. This makes HEMTs exhibit high electron mobility, leading to high-frequency operation. They also have high gain and low noise compared to other FETs. However, HEMTs are expensive to manufacture due to complex manufacturing procedures and material costs.
GaN HEMT
GaN HEMTs are grown on substrates made using either Si, SiC or sometimes GaN. A buffer layer made from AlN is added over the substrate. On the buffer layer, a pure GaN layer is grown. Another layer made from AlGaN forms a heterojunction with the GaN layer. The formation of a high mobility layer “2DEG”, piezoelectric effect, and polarization at the interface of the heterojunction confines high-mobility electrons to enable high-frequency operation.
:quality(80):fill(efefef,0)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/5f/fe/5ffedb2e0ffa6/listing.jpg)
GaN HEMTs are gaining popularity due to their exceptional performance in power electronics and high-frequency applications. They show high thermal stability, and fast switching speed, and exhibit high electron mobility, power density, and breakdown voltage. However, GaN HEMTs are susceptible to high leakage currents, heat, and trapping effects. Commercial applications of GaN HEMT include high-frequency power amplifiers, power switching, power conversion systems, inverters, EVs, LIDARs, radars, mmWave applications, etc.
SiC MOSFET: The top in the market
MOSFET
MOSFET is a widely used semiconductor available in almost every device- from nail-sized small solid-state devices to billions and trillions integrated into a chip. A MOSFET is a type of FET consisting of a n-type or p-type doped channel. The voltage applied at the gate terminal creates an electric field in the channel to control the current flow.
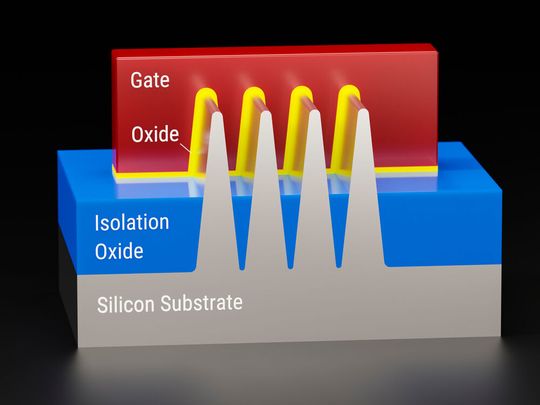
There are various types of MOSFETs: PMOS, NMOS, and CMOS. Each MOSFET type is extensively used in the industry. MOSFETs have high input impedance, scalability, and low heat dissipation and power consumption capabilities. However, MOSFETs are not suitable for high-power applications as they might incur various losses. MOSFETs are widely used to construct semiconductor switches, amplifiers, and integrated circuits or chips.
SiC MOSFET
SiC MOSFETs are constructed in the same as traditional Silicon MOSFETs- but with a SiC substrate instead. Similar to Si MOSFETs, SiC MOSFETs are voltage-controlled devices with three terminals. The voltage at the gate terminal enables controlling current flow to perform a similar but enhanced operation in power electronics. Most SiC MOSFETs operate in enhancement mode compared to depletion mode.
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/f5/e5/f5e5d9e1e9f0511b1cb1403ba940bccc/87420887.jpeg)
BASIC KNOWLEDGE - MOSFET VS. BJT
What’s the difference between MOSFET and BJT?
The use of SiC MOSFETs is increasing in power electronic applications due to wide bandgap properties. SiC MOSFETs exhibit high breakdown voltage, thermal conductivity, and stable high-temperature operation. However, SiC manufacturing and packaging processes are complex and costlier compared to Si MOSFETs. SiC MOSFETs have complex gate drive circuit requirements. SiC MOSFETs are used in power electronics, power supplies, motor drivers, grids, EVs, and many other applications.
GaN HEMT vs SiC MOSFET: What to choose?
Both GaN and SiC are wide bandgap semiconductors. In general, all WBG semiconductors exhibit properties like fast switching, high-temperature tolerance, and low-on-state resistance. In our article about aluminum nitride semiconductor, we have compared the three WBG semiconductors based on properties. The section compares GaN HEMTs and SiC MOSFETs.
| Features | GaN HEMT | SiC MOSFET |
| Bandgap Energy | GaN = 180 W/(m.K) (As a semiconductor) | SiC = 52 W/(m.K) (As a semiconductor) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Very high |
| Thermal Resistance | Lower (1.5x better) | Low |
| Internal Capacitance | Lower | Low |
| Breakdown Voltage | High | Very high |
| Gate Drive Voltage | Low voltage | High voltage |
| Gate Drive Circuit Requirements | Simple | Complex |
| Operating Temperature | High | Very high |
| Switching Speed | Fastest | Slower than GaN |
| Turn ON and Turn OFF Times | Higher than SiC MOSFETs | Slightly lower than GaN HEMTs |
| Power Conversion Efficiency | High | High |
| Power Density | Moderate Suitable for low-voltage and high-frequency applications | Very High Suitable for high-power applications |
| Losses | Low at high frequencies High dead band loss Low off-switching loss | High at high frequencies Low dead band loss High off switching loss |
| Thermal Management | Good | Best |
| Size | Bigger than SiC MOSFETs | Smaller compared to GaN MOSFETs |
| Applications | High-frequency and high-speed switching applications like RF amplification and mmWave applications | Power electronic and renewable energy applications |
The article doesn’t state that GaN HEMTs are better than SiC MOSFETs or SiC MOSFETs are more efficient than GaN HEMTs. It just compares the two emerging semiconductor devices. The performance of GaN HEMT or SiC MOSFET depends upon the choice of product, design, requirements, application, and cost.
References
Power Electronics in the Energy Transition

The parameters for energy transition and climate protection solutions span education, research, industry, and society. In the new episode of "Sound On. Power On.", Frank Osterwald of the Society for Energy and Climate Protection Schleswig‐Holstein talks about the holistic guidance his organization can provide.
Listen now!
(ID:50196781)



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/2f/f3/2ff3221bf7665de2d0acf83760bfd1fa/0130031523v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/c3/16/c316e955a97f5d72d9678297b237b9e5/0129932858v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ef/0a/ef0adb0acf793fe147cc27c21f6a7a67/0129954238v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/53/f9/53f9301dfc9292d02960f7996c79cc6e/0129927601v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6e/cd/6ecd41d095d5111cf4ed37b714844487/0129930878v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/02/c0/02c0e9722f70b1134dbf96fb59a9c73d/0129655179v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/cc/67/cc670ea2029cd2af5c641af70e1bf734/0129816392v4.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ea/e6/eae6aee30071e67a5627027974437134/0129544613v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b1/5e/b15ee02b0ba02db70cf61e37d66ad1d3/0129349127v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/26/d5/26d591cc340077026eac56a0e7564faf/0129949603v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4d/e0/4de02f76a37cbb3df30dd231de589c8e/0128866890v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/18/0b/180b7b63afc91e523592d8a5ce161c96/0129847487v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/be/c8/bec8d43fc0ee73414274be44608b2970/0129748903v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/23/ee/23ee4a97790d6009dbfd7d9577ffa723/0129220424v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3c/d1/3cd1cacbceb792ba63727199c61ca434/0127801860v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/5a/a0/5aa0436498af618297961fd54ab36cdf/0126290792v2.jpeg)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/63/c7/63c7da97be945/diotec.png)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/5f/71/5f71d5f92a5f6/2000px-rogers-corporation-logo-svg.png)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/66/8b/668becd1c07eb/dowa-logo-word--1-.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b9/18/b918d8d0e447a18f7b9e983c25b96330/0125855402v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4d/e0/4de02f76a37cbb3df30dd231de589c8e/0128866890v2.jpeg)