BASIC KNOWLEDGE Conduits of connection: The central role of bus bars in electronics
Related Vendors
An electrical bus bar is an integral part of the electrical power distribution system. Do you know that a bus bar system distributes electric power in a multi-story building? This article details bus bars with their types and applications.
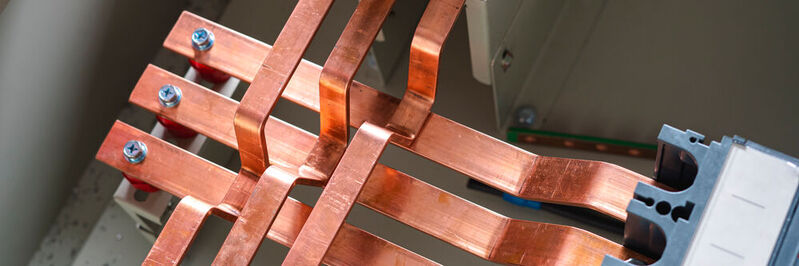
What is a bus bar?
An electrical bus bar is a solid-state conductor made from copper and aluminum- present in the industry for over 150 years. Most bus bars are enclosed in switchboards, panels, distribution stations, ducts, and storage units.
Definition electrical bus bar
An electrical bus bar is a solid conductor that carries high-rated electrical current in switchgear, panels, busway enclosures, main grounding systems, and various power distribution stations. Simply put, a bus bar is a flat-rigid metallic strip or bar that is wider but much shorter than cables.
What does a bus bar do?
In a power distribution system, a source or a generator generates high power in the order of megawatts to distribute over multiple destinations. The step-up voltage is sent through overhead or underground lines. The voltage is step-down for distribution at the receiving end.
For low-voltage distribution with high current ratings, solid-state conductors are preferred. These solid-state conductors are called bus bars. A bus bar can conduct and ground electricity. It is important to note that a bus bar neither converts electrical current nor steps up/down the voltage.
A bus bar offers a low electrically resistant path to incoming or outgoing currents. Bus bars are deployed in groups called bus bar systems, which are used in electrical power distribution panels to distribute electric power. Even high-voltage systems implement bus bars to carry high-rated current.
The reason for choosing bus bars in power distribution systems is less resistance, very low-voltage drop, fewer losses, and better current handling capacity compared to lossy cables. However, bus bars exhibit the skin effect at high current ratings and dissipate large amounts of heat.
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ca/31/ca31c09d6ad7638bed71ac58c1109b24/87335780.jpeg)
BASIC KNOWLEDGE - ALTERNATING CURRENT
What is alternating current?
Bus bar types
Bus bar types by material
When it comes to electronics, copper and aluminum are two extensively used conductive materials. Similarly, the most common material to construct an electrical bus bar is either copper or aluminum.
Copper bus bars
In the periodic table, copper (Z = 29) is the second most conductive element after silver. The conductivity of copper is about 5.96 x 107 S/m. Copper has a high continuous operating temperature above 100 degrees Celsius. The excellent electrical and thermal conductivity enables copper to serve as a conductor in multiple applications.

Rigid and heavy copper bus bars are deployed in indoor and outdoor locations extensively. A copper bus bar is used in corrosive areas near the sea because copper is highly corrosion-resistant and less prone to salinity. Acidic environments and chemically aggressive and humid locations cannot erode copper faster. Implementations in such areas reduce the need for maintenance and replacement of copper bus bars.
Copper bus bars are electroplated with metals such as tin, nickel, and silver to prevent oxidation. A tinned copper bus bar is a common type of bus bar in the market. The transportation industry implements tinned copper bus bar systems in electric locomotives and EVs. However, a copper flat bar has limitations like its high price and energy loss through heat dissipation.
Aluminum bus bars
Aluminum (Z = 13) stands at the fourth number in electrical conductivity after silver, copper, and gold. The conductivity of aluminum is about 3.5 x 107 S/m. aluminum has a slightly lower continuous operating temperature than 100 degrees Celsius.
Aluminum bus bars were first manufactured in the late nineteenth century. An aluminum bus bar is lightweight, flexible, and easier to bend for various applications. The cost of handling and installing aluminum bus bars is much lower than copper bus bars.
Similar to a tinned copper bus bar, an aluminum bus bar is electroplated with metals such as tin, nickel, or silver. Electroplating an aluminum bus bar system reduces galvanic corrosion and improves stability, efficiency, and overall performance. A nickel-plated aluminum bus bar has improved contact-based characteristics.
Aluminum bus bars exhibit less skin effect, leading to less alteration of the heating pattern. However, aluminum bus bars have certain disadvantages like high thermal expansion/contraction, susceptibility to corrosion, poor thermal conductivity, and lesser current carrying capability than a copper flat bar.
Bus bars by shape
Regardless of the material used, the shape of the electrical bus bar is one of the factors that affect current ratings. The bus bar shape influences the skin effect, eventually affecting the overall resistance, current carrying capability, and heat dissipation.
Rigid bus bars (Flat bars)
A rigid bus bar is flat in shape and physically hard in appearance. Generally, copper bus bars are a type of rigid bus bars. The heavyweight and inflexible behavior of a copper flat bar is the reason for such classification. Rigid busbars are used in transportation, switchgear, and substations.
Flexible bus bars (Flexi bars)
A flexible busbar or a flexi bar is a bus bar that can be easily bent and converted into desirable configurations. Depending upon industrial applications, flexi bars are used in areas where flexibility is needed. Usually, thin strips of aluminum bus bars are laminated together to create a bus bar system.
Round bus bars
Round bus bars are either circular or cylindrical in shape. A round bus bar can either be hollow or solid inside. Round bus bars have a lesser area of cross-section, leading to an increase in skin effect. As a result, round bus bars eventually exhibit higher resistance compared to flat bars of the same size and material.
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/67/a9/67a9bfa6e215f2657331765672a43be5/86165585.jpeg)
BASIC KNOWLEDGE - SEMICONDUCTORS
What you need to know about power semiconductors
Bus bars by phase
A phase in an electrical bus bar system typically represents a single bus bar strip. However, the bus bar phase is also related to electrical power distribution. Bus bar systems use more than one busbar per phase. Due to the skin effect, outer bus bars in a bus bar system carry most of the current.
Single-phase bus bar
A single phase bus bar distributes electric power in a single phase system. It has one live and one neutral conductor. Simply put, a single phase bus bar carries single phase current to lightning equipment and appliances in smaller locations.
Three-phase bus bar
A three phase bus bar system carries a high-rated three-phase power in industrial applications. Compared to the single-phase bus bar system, the three-phase bus bar system is larger because it contains three live and one neutral conductor.
Bus bars by construction type
The spacing of bus bars in a bus bar system influences the skin effect. The asymmetrical distribution of bus bars results in high operating temperatures. This phenomenon is called the proximity effect in bus bars. Increasing the distance between each bus bar, about standard 300 mm, decreases the overall resistance and mechanical effects of faulty current.
Non-segregated bus bars
In a non-segregated bus bar system, bus bar phases are not separated from each other. There is a separation between the phases and the enclosure. The non-segregated busbar systems are used in small-scale low-voltage applications including alternators and transformers.
Segregated bus bars
Electrical bus bar phases are separated from each other through a barrier. There is also a separation between the phases and the enclosure. The segregated busbar systems exhibit reduced proximity and skin effect to offer uniform current distribution and high ratings.
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/50/47/5047818bfeb5d315d1db5c5946dbdeae/0116669487.jpeg)
POWERING THE FUTURE
How electrification is driving the world in 2024
Bus bar types by insulation
Insulated bus bars
An electrical bus bar can be insulated through PVC, polyester, epoxy, and various other insulating materials. Insulation increases the size of the enclosure of bus bars. Insulating materials stacked between multiple bus bars offer a sandwich-like busbar system to decrease the overall size. High-current applications use insulated bus bars for safety reasons. Irrespective of the current rating, insulated bus bars are commonly seen in densely populated areas.
Non-insulated bus bars
In general practice, most electrical bus bar systems have no insulation. Sometimes, insulating pillars or support could be present between non-insulated busbars. Bus bar systems in industries and factories have no insulation. Most ground bus bars are non-insulated. The reason for the non-insulation of busbars is that common people do not visit such areas except certified professionals. However, non-insulation can cause serious accidents due to easy, access, touching, and handling.
Bus bar types by location of implementation
Indoor bus bars
Indoor bus bars are deployed inside the premises. Most aluminum bus bar systems are used indoors compared to copper bus bars for their low current ratings and flexibility. However, a copper flat bar system is also used inside multi-story buildings.
Outdoor bus bars
Outdoor busbars are deployed outside of the premises on open grounds. Copper bus bar systems are used outdoors because they do not expand in heat, experience less damage in UV rays, and are less susceptible to corrosion than aluminum busbars.
Vertical bus bars
Vertical bus bar systems typically distribute current in a multi-story building “vertically”. The current rating in such distributions is the highest at lower floors compared to a slight decrease at higher levels.
Horizontal bus bars
A horizontal busbar system distributes electrical power “horizontally” over long distances. The horizontal bus bar system runs on the same level, either below the ground or slightly below the ceiling.
:quality(80):fill(efefef,0)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/5f/fe/5ffedb2e0ffa6/listing.jpg)
Bus bar types by application area
Distribution bus bars
Distribution bus bar systems take electrical power from incoming feeders and distribute it to outgoing feeders. Both incoming and outgoing electrical currents meet at a distribution bus bar. In simple words, distribution bus bars “carry” incoming electrical current from source generators and distribute the outgoing electrical power to various circuits.
Collector bus bars
A collector bus bar system “distributes” electric power to a storage system. Such a system can look like it collects electric power but in reality, it distributes electric power to a unit that stores it. Collector busbars are used in renewable energy projects such as battery bus bars of series and parallel configurations.
Ground bus bars
In addition to distributing current in power systems, bus bars function as a central point for ground connections. Electrical bar systems known as ground bus bars are used to connect various conductors and components to the main grounding point. Ground bus bars ensure the safety and prevention of shocks and short circuits.
Applications of Bus bars in Power Electronics
Switchgear
The most common implementation of electrical bus bars is with switchgear. Bus bars distribute current to various relays, circuit breakers, fuses, and other components. Electrical busbars function closely with circuit breakers through correct load distribution to cut off the faulty current.
Bus ducts
Electrical bars are housed inside a metal enclosure, known as a bus duct, with suitable coverings, insulation, and support. Bus ducts distribute power to multiple locations over long distances through underground or overhead implementation. Simply put, bus ducts are conduits that contain groups of electrical bus bars.
Power transmission
Electrical bar systems are used for electrical power distribution to various locations inside a building. Depending upon the arrangement, a vertical and horizontal bus bar system distributes power.
High-power applications
Electrical bus bar systems distribute power in power supply systems. High-rated current is distributed through non-insulated bus bars for either a high-voltage or a low-voltage application in factories.
Renewable power plants
Electrical bar systems are used in renewable energy sources like wind turbines, solar panels, and batteries. Battery bus bars are commonly used for electromobility in automotive applications.
(ID:49980545)



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/71/fd/71fdcc22d9a9bd2f42985f692c4aefa2/0128924236v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/94/54/94548eaecd020681e558d563bc48ba1d/0128926221v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/29/99/2999bb9af245dd31f4c837c1d9359046/0128923137v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/10/78/107856328ef320cc081bf88e0baf95e8/0128685487v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/67/62/676279913d77e1db48eb5cbe9be4c767/0128937895v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/0f/a2/0fa2b5bdc21e408fd73e637d226d5210/0128681532v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4f/6f/4f6faf0ca6f748a2967d6b5bba7c88e1/0128682406v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ad/52/ad52f7b5542eff15ba54ec354d31b50d/0128681536v4.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1e/9c/1e9c45d6fcf2fb48dc47756e4cb20174/0128931043v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/8b/42/8b4271e1bedea432ab03c83959e30431/0128818204v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/87/5a/875a8fa395c1eec9677e075fae7f5e8e/0128793884v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/2f/93/2f9364112e8c6ff38c26f9ba34d0f692/0128791306v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3c/d1/3cd1cacbceb792ba63727199c61ca434/0127801860v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/5a/a0/5aa0436498af618297961fd54ab36cdf/0126290792v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/cb/30/cb30ebdca7fcaea281749cb396654eb3/0124716339v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/0b/b4/0bb4cdfa862043eac04c6a195e59b3e0/0124131782v2.jpeg)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/5f/71/5f71d5f92a5f6/2000px-rogers-corporation-logo-svg.png)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/68/2c/682c3e2e9a195/logotype-rvb.jpeg)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/66/8b/668becd1c07eb/dowa-logo-word--1-.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/99/c9/99c9a4799394750fd1a9a51890c948ad/0124997234v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/f0/a4/f0a4ec50e99b87afad613593f0f0860b/0124997238v4.jpeg)